
Welcome to another enlightening edition of Ndlalane health newsletters! Today, we delve into the intriguing world of men's health, specifically focusing on a condition that affects countless individuals worldwide – erectile dysfunction, commonly known as ED. Join us as we uncover the mysteries surrounding this condition. Surprisingly, ED is not just an issue for older men - it is increasingly affecting younger men too. In this article, we dive deep into the world of ED among young men, exploring its causes, treatment options, and ways to improve overall sexual wellness and quality of life.
Let’s define ED, but first let me remind you of an important disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Now that, this is out of the way, let’s continue. So, erectile dysfunction can be defined as, the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection for satisfactory sexual performance. It is not just an isolated single event but an ongoing recurrence which can significantly impact a man's self-esteem, relationships, and overall well-being. ED has long been associated with older age but recently research shows that young men are increasingly affected. Factors such as inappropriate habits like excessive masterbation, stress, certain medications, being overweight, sedentary lifestyle, substance abuse, and psychological issues like performance anxiety contribute to ED among this vulnerable group of young men. What do we mean by young men? The ballpark number for a young man, is male person below the age of 40 years.
Let’s take a moment to explain an erection before we get to its dysfunction. The mechanics of male erections are an intricate interplay of hormonal, vascular, and neural factors that lead to increased blood flow and engorgement of erectile tissue. I will use a bit of jargon to explain, please try to follow through, but I will be as simple as possible. There are several steps involved in order for the man to get an erection;
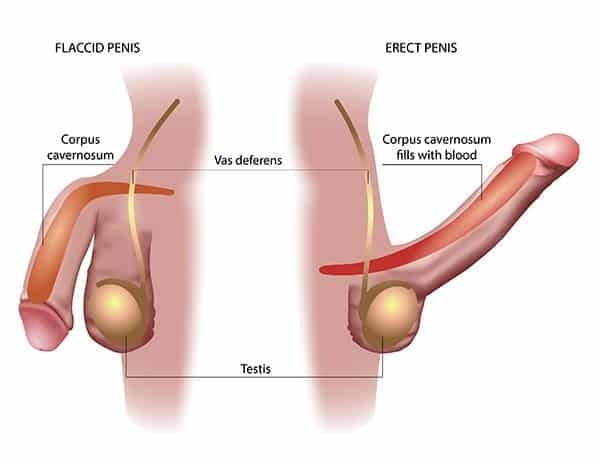
1. Sexual arousal: The first step in getting an erection is sexual arousal. This can be triggered by various factors such as visual, auditory, or tactile stimuli, or by thoughts or fantasies. Sexual arousal leads to the release of neurotransmitters such as nitric oxide and acetylcholine, which signal the brain's desire for sexual activity.
2. Nitric oxide release: Nitric oxide (NO) is a potent vasodilator that causes the relaxation of smooth muscle cells, allowing blood to flow into the penis.
3. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) Increase: As the blood flows into the penis it triggers an increase of another hormone called Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which is crucial in the expansion of blood vessels.
4. Penile engorgement: Both the Smooth muscle relaxation and blood vessels expansions causes the penis to become engorged. This engorgement puts pressure on the veins that carry blood away from the penis, causing them to constrict and preventing blood from leaving the penis.
5. Penile erection: Blood continues to flow into the penis, it becomes increasingly engorged, leading to a penile erection. The erection is maintained by the continued relaxation of smooth muscle cells and the continued constriction of veins.
6. Ejaculation: Lastly ejaculation is the release of semen from the penis during sexual activity. It is triggered by the stimulation of the sensory nerves in the penis, which send signals to the brain, leading to the release of hormones that cause the muscles in the pelvic area to contract, forcing semen out of the penis.
This is an over simplified explanation of the mechanism of action of an erection, but keep in mind that there are many other factors that can influence the process, such as psychological and social factors, as well as medical conditions that can affect the ability to achieve and maintain an erection.
Alright now that you understand all that, let’s begin the adventures of ED.
Picture this: a man, full of vigor and vitality, ready to conquer the world. Suddenly, a glitch occurs, and his confidence wavers. That glitch is none other than erectile dysfunction. Like I said in the beginning, ED is a condition that affects a man's ability to maintain or achieve an erection necessary for satisfactory sexual performance. It can arise from various causes, both physical and psychological, and can have a significant impact on a man's self-esteem and overall well-being.
How can a man find themselves here? Let’s looks at some of the common causes that can result in ED, please bear in mind that understanding the root causes of ED is crucial in finding effective solutions. While it is often associated with age, ED can affect men of all ages. Here are some common factors:
1. Physical Factors:
- Cardiovascular diseases and high blood pressure
- Diabetes and obesity
- Hormonal imbalances, such as low testosterone levels
- Neurological disorders
- Certain medications and substance abuse
2. Psychological Factors:
- Stress, anxiety, and depression
- Relationship problems
- Performance anxiety
- Past trauma or sexual abuse
3. Lifestyle Factors:
- Sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity
- Poor diet and nutrition
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Sleep disorders and chronic fatigue
Since the title of the article is ED in young, men, I wanted to highlight some of the root causes which are specific to young men. You can find that a 24 years old man is suffering from ED, and you ask yourself, how is this possible? This person is supposed to be at their sexual prime. Here is the devil to the matter, excessive or compulsive masturbation amongst young men who are still adjusting to their introduction to sexual hormones coursing through their bodies. It's worth mentioning that the concept of overmasturbation and its specific effects on sexual health are not widely studied in scientific literature. The available information is largely anecdotal, and individual experiences can vary greatly. It's always a good idea to approach the topic with an open mind and seek professional advice when needed.
Generally speaking however, this habit has been associated with temporary sexual dysfunction in some individuals, and this could be due to factors such as physical fatigue, desensitization of the genitals, or a temporary imbalance in neurotransmitters and hormones involved in sexual arousal. This in turn result in decreased sexual desire or libido. It can occur if the individual becomes desensitized to sexual stimuli or if the excessive masturbation causes a sense of dissatisfaction or apathy towards sexual activities.
In a perfect world these effects should typically be temporary and resolve when masturbation habits are moderated. The body has a remarkable ability to heal and restore its normal functioning however the other aspect of performance anxiety and confidence tend to kick in and make the temporary experience a negative cascade which exacerbates the erectile dysfunction, throwing the young man into a spiraling crisis of depression and anger outbursts.
If you're experiencing persistent or concerning sexual difficulties, it's recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a urologist or a sexual health specialist, who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate guidance.
The second most potent risk factor of ED in young men is excessive alcohol abuse and smoking. It has become a culture for men, to treat alcohol like some everyday or every weekend sporting adventure that they must partake in. If I take you back to the beginning of the article, we understand the importance of blood flow during an erection process, and what alcohol does is;
1. Reduced blood flow: Alcohol is a vasodilator, meaning it relaxes and widens blood vessels. While this can lead to temporary feelings of relaxation and lowered inhibitions, excessive alcohol consumption can hinder blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve and maintain an erection.
2. Hormonal changes: Alcohol can disrupt the balance of hormones in the body, including testosterone. Testosterone is crucial for maintaining sexual desire and performance. Excessive alcohol consumption can lower testosterone levels, which may contribute to ED.
3. Nerve damage: Long-term heavy drinking can cause nerve damage, known as peripheral neuropathy. This damage can affect the nerves involved in sexual arousal and can impair the ability to achieve and sustain an erection.
4. Psychological factors: Alcohol can impact mental and emotional well-being. Excessive alcohol consumption may lead to anxiety, depression, and relationship problems, all of which can contribute to ED.
5. Performance anxiety: Alcohol can impair judgment and increase feelings of self-consciousness. This can lead to performance anxiety, which can further exacerbate erectile difficulties.
I feel we know enough for today 😊, let’s navigating the Landscape of treatment Options. Fortunately, ED is a treatable condition, and there are various options available to help men regain their sexual function and confidence. Here are some potential solutions: key word here is potential solutions. I cannot stress enough the importance of getting personalised treatment options from your health care professional.
1. Medications:
Oral medications, such as Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra, are often prescribed to enhance blood flow to the penis.
Alprostadil, a medication available in different forms (injection, suppository, or cream), can also be used to stimulate blood flow.
2. Lifestyle Modifications:
Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can positively impact erectile function.
Managing stress levels and seeking therapy for psychological factors can also be beneficial.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve overall sexual health.
3. Counseling and Therapy:
Discussing ED with a healthcare professional or therapist can help address any underlying psychological issues and provide guidance for effective coping mechanisms.
Couples therapy may be beneficial for addressing relationship problems that contribute to ED.
Discussing sexual health with your child is very crucial as a parent or guardian.
In conclusion, 😊 yes you have made it to the end of the article and congratulations, your curiosity has made you gain valuable information. Don’t forget to share this with your friends and family so that they can also be in the know like you, through Ndlalane Health. You can comment and or add questions by replying directly to this email if you're a subscriber. Subscription is free and all you have to do is add your email to the subscribers list on our website. Click here to access the link for your convenience.
Back to the conclusion, let’s summarize quickly, while the journey through erectile dysfunction may seem daunting, it's important to remember that there is hope. Seeking professional help and exploring the available treatment options can lead to positive outcomes and restored sexual satisfaction. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources and support systems available to guide you towards a fulfilling and healthy sex life.
We hope this article has shed some light on the often-misunderstood topic of erectile dysfunction. By understanding the causes and treatment options for ED, you can take control of your sexual health and improve your overall well-being. Stay tuned for more informative articles on men's health through Ndlalane Health Newsletters, as we continue to explore various aspects that contribute to a fulfilling and thriving life.
Stay informed, stay healthy, and until next time, take care!
References:
1. Shamloul, R., & Ghanem, H. (2013). Erectile dysfunction. The Lancet, 381(9861), 153-165.
2. Hatzimouratidis, K., et al. (2016). EAU Guidelines on Erectile Dysfunction: An Update. European Urology, 71(4), 618-629.
3. Capogrosso, P., et al. (2013). One Patient Out of Four with Newly Diagnosed Erectile Dysfunction Is a Young Man—Worrisome Picture from the Everyday Clinical Practice. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 10(7), 1833-1841.
4. Serefoglu, E. C., et al. (2016). Age, Sexual Behavior, and Seminal Oxidative Stress among Men with Primary Lifelong Premature Ejaculation: Is There an Association? Andrologia, 48(5), 513-518.
5. Corona, G., et al. (2014). Psychological and Interpersonal Dimensions of Sexual Function and Dysfunction. The Journal of Sexual Medicine, 11(9), 2097-2128.
6. Nehra, A., & Jackson, G. (2016). Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Disease: Efficacy and Safety of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors in Men with Both Conditions. European Heart Journal, 37(31), 2456-2469.

